1 Like

Vite 源码解析(2) - 模块依赖图
由于现代前端都是模块化开发, 因此各个模块之间会产生各种各样多对多的依赖关系. 为此, 各个打包器都要以 entry 作为起点, 去寻找整个 APP 的模块依赖图. vite 也不例外, 我们这篇文章就来学习下 vite 的 ModuleGraph 是如何实现的.
ModuleGraph 实例
在 createServer 中, 我们看到会创建一个 ModuleGraph 实例, 并把它作为参数传递到 `createPluginContainer`(我们下一章重点来讲 vite 的插件机制) 函数中, 供一些插件使用. 此外, 该实例也会传递到 `devServer`(我们下下章重点来讲 vite 的开发服务及中间件机制) 对象中, 供后续的 HMR 等使用.
const moduleGraph: ModuleGraph = new ModuleGraph((url, ssr) => container.resolveId(url, undefined, { ssr }) ); const container = await createPluginContainer(config, moduleGraph, watcher); const server: ViteDevServer = { config, middlewares, httpServer, watcher, pluginContainer: container, ws, moduleGraph, // ... };
ModuleNode
ModuleNode 是每个模块节点的原子信息, vite 正是通过它将所有的模块关联起来, 形成模块依赖图. 下面我们来简单介绍下各个属性.
export class ModuleNode { url: string; // 以 / 开头的相对路径 id: string | null = null; // 模块的绝对路径, 但可能带着 hash 和 query file: string | null = null; // 模块的绝对路径, 不带 hash 和 query type: "js" | "css"; // 如果路径上带着 &direct, 则为 css, 否则为 js info?: ModuleInfo; // 模块信息, 来自 rollup, 有 ast, 源码字符串等, 详情: https://rollupjs.org/guide/en/#thisgetmoduleinfo meta?: Record<string, any>; // 自定义的元信息 importers = new Set<ModuleNode>(); // 导入当前模块的模块的集合 importedModules = new Set<ModuleNode>(); // 当前模块的导入模块集合(或者说谁用到) acceptedHmrDeps = new Set<ModuleNode>(); // 接收的热更新依赖的集合, 我们放在热更新那一章来讲 isSelfAccepting?: boolean; // 是否为模块自更新 transformResult: TransformResult | null = null; // 通过插件构建后的结果 ssrTransformResult: TransformResult | null = null; ssrModule: Record<string, any> | null = null; ssrError: Error | null = null; lastHMRTimestamp = 0; // HMR 最后更新时间, 也就给给模块 url 上附上 &t=xxxxxxxxxxxxx 的那个时间戳 lastInvalidationTimestamp = 0; // 最后失效的时间, 如果你的模块时间戳超过它, 说明就过期了 constructor(url: string) { this.url = url; this.type = isDirectCSSRequest(url) ? "css" : "js"; // 判断是 js 还是 css, 注意这里的 css 也可能是 sass, less 等等 // #7870 // The `isSelfAccepting` value is set by importAnalysis, but some // assets don't go through importAnalysis. // 过滤掉 html 文件和不需要被导入分析的模块(json, sourcemap, direct css) // 这些模块不需要关注自更新 if (isHTMLRequest(url) || canSkipImportAnalysis(url)) { this.isSelfAccepting = false; } } }
ModuleGraph 各个属性, 方法一览
export class ModuleGraph { urlToModuleMap: Map<string, ModuleNode>; // key 为相对路径, value 为 ModuleNode 的集合 idToModuleMap: Map<string, ModuleNode>; // key 为模块的绝对路径(但可能带着 hash 和 query), value 为 ModuleNode 的集合 fileToModulesMap: Map<string, Set<ModuleNode>>; // key 为模块的绝对路径(不带 hash 和 query), value 为 ModuleNode 的集合 safeModulesPath: Set<string>; // 哪些模块是安全模块, 后面讲 importAnalysis 插件时再做讲解 constructor( private resolveId: ( url: string, ssr: boolean ) => Promise<PartialResolvedId | null> ); async getModuleByUrl( rawUrl: string, ssr?: boolean ): Promise<ModuleNode | undefined>; getModuleById(id: string): ModuleNode | undefined; getModulesByFile(file: string): Set<ModuleNode> | undefined; onFileChange(file: string): void; invalidateModule( mod: ModuleNode, seen?: Set<ModuleNode>, timestamp?: number ): void; invalidateAll(): void; async updateModuleInfo( mod: ModuleNode, importedModules: Set<string | ModuleNode>, acceptedModules: Set<string | ModuleNode>, isSelfAccepting: boolean, ssr?: boolean ): Promise<Set<ModuleNode> | undefined>; async ensureEntryFromUrl(rawUrl: string, ssr?: boolean): Promise<ModuleNode>; createFileOnlyEntry(file: string): ModuleNode; resolveUrl(url: string, ssr?: boolean): Promise<ResolvedUrl>; }
urlToModuleMap
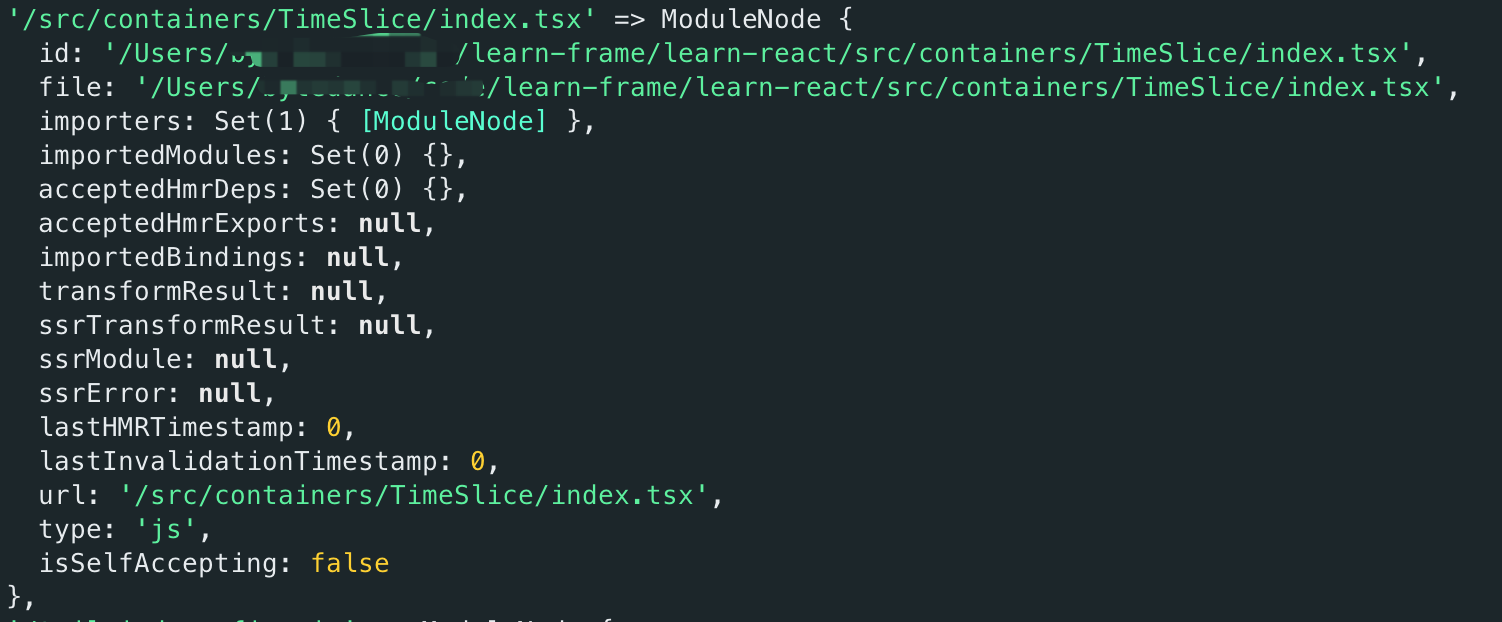
idToModuleMap
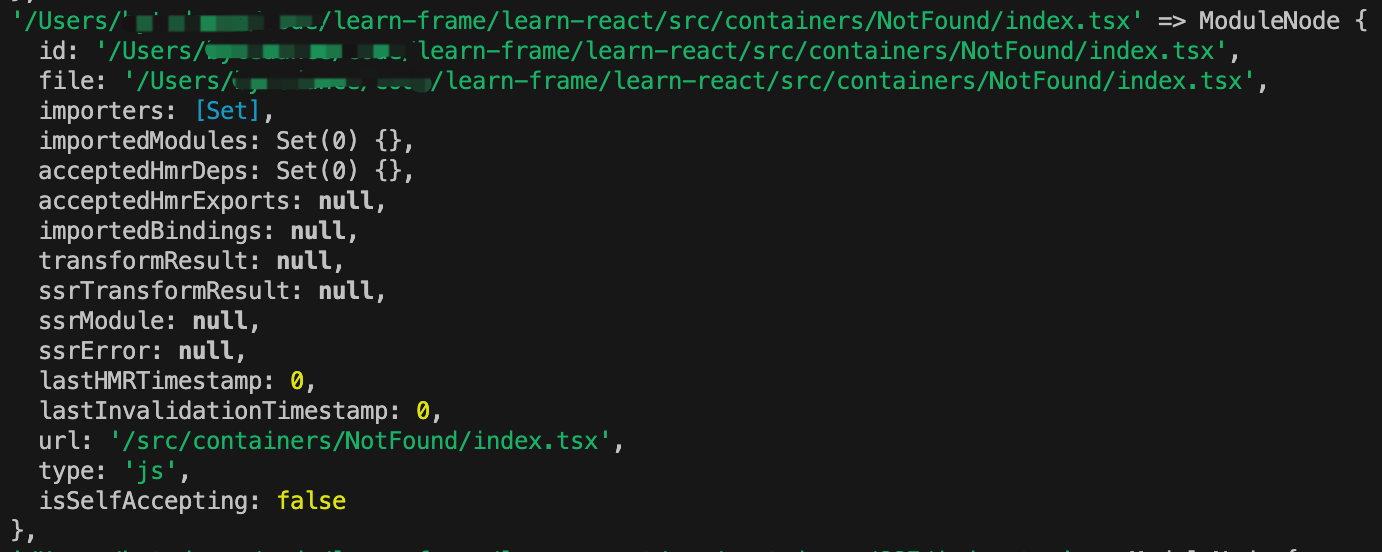
fileToModulesMap
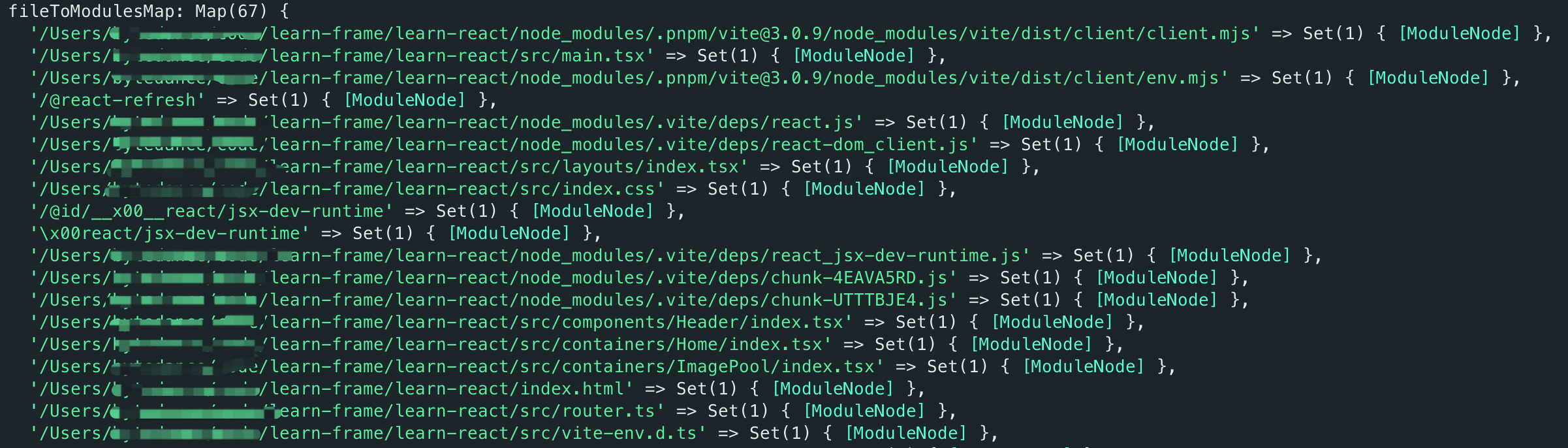
safeModulesPath
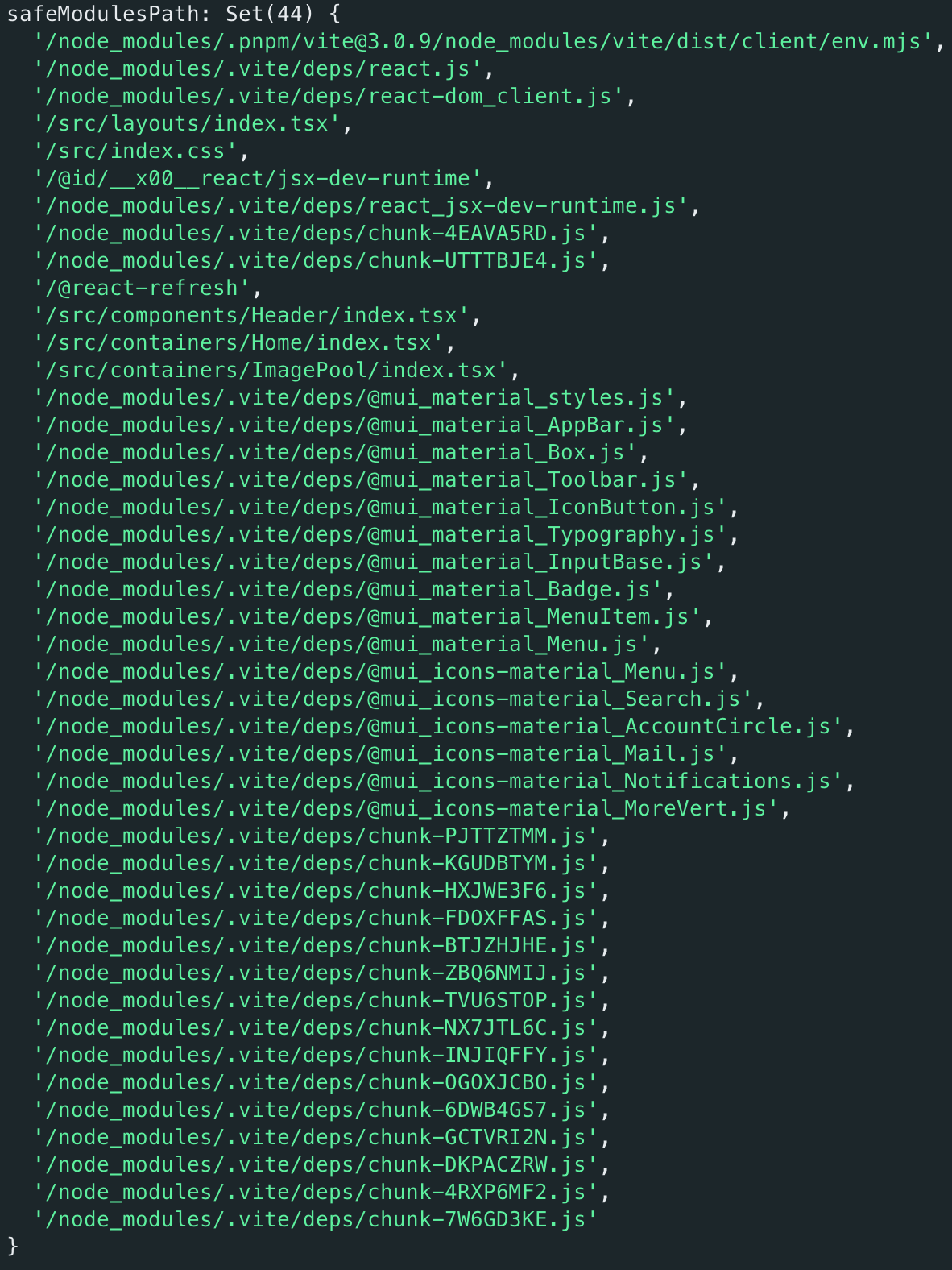
getModuleByUrl
根据一个 url 获取对应的 ModuleNode. url 为模块的相对路径.
export class ModuleGraph { async getModuleByUrl( rawUrl: string, ssr?: boolean ): Promise<ModuleNode | undefined> { const [url] = await this.resolveUrl(rawUrl, ssr); return this.urlToModuleMap.get(url); } }
getModuleById
根据一个 id 获取对应的 ModuleNode. id 为模块的绝对路径(可能带着 hash 和 query)
export class ModuleGraph { getModuleById(id: string): ModuleNode | undefined { // 我们知道 vite 为了判断源码模块的新鲜度. 给 url 加了一个 ?t=xxxxxxxxxxxxx // removeTimestampQuery 就是把这个 query 去掉 return this.idToModuleMap.get(removeTimestampQuery(id)); } }
getModulesByFile
根据一个 file 获取对应的 ModuleNode 集合. file 为模块的绝对路径(不带 hash 和 query).
export class ModuleGraph { getModulesByFile(file: string): Set<ModuleNode> | undefined { return this.fileToModulesMap.get(file); } }
onFileChange
当文件发生变化时, 就把旧的文件批量过期掉.
export class ModuleGraph { onFileChange(file: string): void { const mods = this.getModulesByFile(file); if (mods) { const seen = new Set<ModuleNode>(); mods.forEach((mod) => { this.invalidateModule(mod, seen); }); } } }
invalidateModule
将模块过期, 思路很简单, 把时间改了即可.
export class ModuleGraph { invalidateModule( mod: ModuleNode, seen: Set<ModuleNode> = new Set(), timestamp: number = Date.now() ): void { // Save the timestamp for this invalidation, so we can avoid caching the result of possible already started // processing being done for this module // lastInvalidationTimestamp 上面说了, 是最后失效的时间, 如果你的模块时间戳超过它, 说明就过期了 // 所以把当前模块时间戳赋值给 lastInvalidationTimestamp, 那这个模块就过期了 mod.lastInvalidationTimestamp = timestamp; // Don't invalidate mod.info and mod.meta, as they are part of the processing pipeline // Invalidating the transform result is enough to ensure this module is re-processed next time it is requested // 把经过插件转换后的结果废弃掉 mod.transformResult = null; mod.ssrTransformResult = null; invalidateSSRModule(mod, seen); } }
invalidateAll
没啥说的, 循环废掉当前 id 下的所有模块.
export class ModuleGraph { invalidateAll(): void { const timestamp = Date.now(); const seen = new Set<ModuleNode>(); this.idToModuleMap.forEach((mod) => { this.invalidateModule(mod, seen, timestamp); }); } }
updateModuleInfo
当导入关系发生变化时, 需要更新模块之间的关系. 这也是 ModuleGraph 最重要的一个方法.
export class ModuleGraph { /** * Update the module graph based on a module's updated imports information * If there are dependencies that no longer have any importers, they are * returned as a Set. */ async updateModuleInfo( mod: ModuleNode, // 当前模块对应的 ModuleNode 对象 importedModules: Set<string | ModuleNode>, // 当前模块导入的模块 acceptedModules: Set<string | ModuleNode>, // 当前模块接收热更新模块的合集 isSelfAccepting: boolean, // 如果是自身更新则为 true ssr?: boolean ): Promise<Set<ModuleNode> | undefined> { mod.isSelfAccepting = isSelfAccepting; // 先把 importedModules(当前模块导入的模块集合) 保存一份 const prevImports = mod.importedModules; // 创建一个空的 Set const nextImports = (mod.importedModules = new Set()); // 不再导入的模块集合 let noLongerImported: Set<ModuleNode> | undefined; // update import graph // 遍历新的导入的 modules for (const imported of importedModules) { const dep = typeof imported === "string" ? await this.ensureEntryFromUrl(imported, ssr) : imported; // 将当前模块(mod)添加到被导入模块(dep) 的 importer 上 dep.importers.add(mod); // 把这个被导入的模块(dep) 添加到 nextImports 中 nextImports.add(dep); } // remove the importer from deps that were imported but no longer are. prevImports.forEach((dep) => { // 如果 nextImports 中没有这个 dep if (!nextImports.has(dep)) { // 反过来说明 dep 没在当前模块中导入, 所以把 dep 的 importers 删除掉当前 mod dep.importers.delete(mod); // 如果 dep 的 importers 为空 if (!dep.importers.size) { // 说明 dep 没有被任何模块导入, 于是把它归类到 noLongerImported 中 // dependency no longer imported (noLongerImported || (noLongerImported = new Set())).add(dep); } } }); // update accepted hmr deps // 将 import.meta.hot.accept() 中设置的模块添加到 mod.acceptedModules 中 const deps = (mod.acceptedHmrDeps = new Set()); for (const accepted of acceptedModules) { const dep = typeof accepted === "string" ? await this.ensureEntryFromUrl(accepted, ssr) : accepted; deps.add(dep); } // 返回不再被任何模块导入的模块的集合 return noLongerImported; } }
ensureEntryFromUrl
目的就是如果找到这个模块, 就把这个模块返回, 否则创建一个新的 ModuleNode, 并放置到 urlToModuleMap, idToModuleMap, fileToModulesMap.
export class ModuleGraph { async ensureEntryFromUrl(rawUrl: string, ssr?: boolean): Promise<ModuleNode> { const [url, resolvedId, meta] = await this.resolveUrl(rawUrl, ssr); let mod = this.urlToModuleMap.get(url); // 如果没获取 mod if (!mod) { // new 一个新的 ModuleNode mod = new ModuleNode(url); if (meta) mod.meta = meta; // 加入到 urlToModuleMap this.urlToModuleMap.set(url, mod); mod.id = resolvedId; // 加入到 idToModuleMap this.idToModuleMap.set(resolvedId, mod); // 清除掉 hash, query 作为 file const file = (mod.file = cleanUrl(resolvedId)); let fileMappedModules = this.fileToModulesMap.get(file); // 如果没有 fileMappedModules Set if (!fileMappedModules) { // 初始化一个 fileMappedModules = new Set(); this.fileToModulesMap.set(file, fileMappedModules); } // 否则添加进去即可 fileMappedModules.add(mod); } // 返回 mod return mod; } }
createFileOnlyEntry
对于像 @import 这种也要放在模块依赖图中.
export class ModuleGraph { // some deps, like a css file referenced via @import, don't have its own // url because they are inlined into the main css import. But they still // need to be represented in the module graph so that they can trigger // hmr in the importing css file. createFileOnlyEntry(file: string): ModuleNode { file = normalizePath(file); let fileMappedModules = this.fileToModulesMap.get(file); if (!fileMappedModules) { fileMappedModules = new Set(); this.fileToModulesMap.set(file, fileMappedModules); } const url = `${FS_PREFIX}${file}`; for (const m of fileMappedModules) { if (m.url === url || m.id === file) { return m; } } const mod = new ModuleNode(url); mod.file = file; fileMappedModules.add(mod); return mod; } }
resolveUrl
export class ModuleGraph { // for incoming urls, it is important to: // 1. remove the HMR timestamp query (?t=xxxx) // 2. resolve its extension so that urls with or without extension all map to // the same module // 1. 去掉热更新带着的 import=xxxx 和 ?t=xxxxxx 参数 // 2. 解析其扩展名,以便带有或不带有扩展名的 url 都映射到同一个模块 async resolveUrl(url: string, ssr?: boolean): Promise<ResolvedUrl> { url = removeImportQuery(removeTimestampQuery(url)); // resolveId 是 rollup 插件体系的, 它就是获取当前模块在文件系统的绝对路径, 下一章讲插件会说到 const resolved = await this.resolveId(url, !!ssr); const resolvedId = resolved?.id || url; const ext = extname(cleanUrl(resolvedId)); const { pathname, search, hash } = parseUrl(url); if (ext && !pathname!.endsWith(ext)) { url = pathname + ext + (search || "") + (hash || ""); } return [url, resolvedId, resolved?.meta]; } }

PREVIOUS POST
Vite 源码解析(1) - 配置篇

NEXT POST
Vite 源码解析(3) - 插件篇